What are the benefits of using rigid PCB technology?
Rigid PCB technology offers numerous advantages in modern electronics. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global rigid PCB market is projected to reach USD 32.5 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing demand for rigid printed circuit boards across various sectors, including automotive and consumer electronics. One key benefit of rigid PCBs is their robustness. They provide good structure and support for complex electronic components.
Moreover, rigid PCBs enable efficient heat dissipation. This quality is essential in high-performance devices where thermal management is critical. A study from IPC indicated that over 70% of electronic failures are related to thermal issues. Thus, using rigid PCB technology can enhance device reliability significantly.
Despite its advantages, rigid PCB technology poses some challenges. The initial cost can be higher compared to flexible alternatives. Also, once designed, making changes to the layout can be difficult. Understanding these aspects is crucial for manufacturers as they navigate production decisions. Ultimately, the benefits of rigid PCBs can lead to greater product integrity and performance in a competitive market.

Benefits of Rigid PCB Technology in Modern Electronics
Rigid PCB technology plays a vital role in modern electronics. It offers exceptional stability and durability. These boards can handle high performance in various applications. A recent industry report notes that the rigid PCB market is expected to reach $25 billion by 2026. This growth reflects their critical role in sectors like telecommunications and consumer electronics.
One significant advantage is their ability to support complex circuits. Rigid PCBs allow for more precise routing of electrical signals. They minimize electromagnetic interference, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity. For instance, their use in smartphones improves functionality and reliability. However, designing these PCBs can be challenging. Engineers must balance performance with manufacturing costs, which requires careful planning.
Tips: When designing your rigid PCB, consider thermal management. Overheating can affect performance. Use materials that dissipate heat effectively. Also, think about layout simplicity. Complicated designs can increase production time and costs. Keep it simple for better efficiency.
Enhanced Durability and Reliability of Rigid PCBs

Rigid PCB technology offers significant benefits, particularly in terms of durability and reliability. These boards are constructed from solid materials that withstand physical stress, temperature fluctuations, and environmental factors. This resilience ensures longevity in various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. A robust design decreases the likelihood of failures and enhances overall performance.
Tips: When selecting rigid PCBs, consider the operating environment. High humidity or extreme temperatures may require specialized materials. Always review design specifications carefully to avoid issues during production.
The structural integrity of rigid PCBs supports complex circuits without warping or bending. This stability is crucial for high-density applications where space is limited. However, imperfect designs can sometimes lead to unexpected failures. Designers must be meticulous to prevent these pitfalls. Small errors in layout can have large repercussions, complicating repairs or replacements.
Design Flexibility and Miniaturization in Rigid PCB Applications
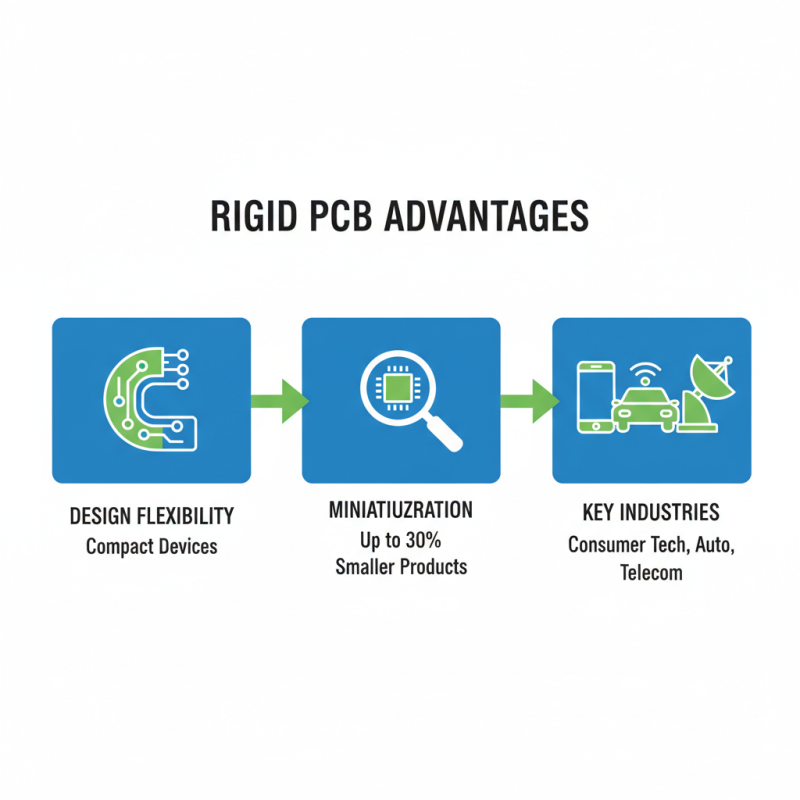
Rigid PCB technology offers significant advantages, particularly in design flexibility and miniaturization. In industries like consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications, the push for compact devices is relentless. Rigid PCBs can be engineered to fit tighter spaces without compromising functionality. Reports indicate that these boards can reduce overall product size by up to 30% while maintaining performance.
The high degree of precision in rigid PCB design allows for intricate circuit layouts. Designers can utilize multi-layer configurations to integrate pathways and components more efficiently. In turn, this leads to enhanced thermal performance and effective signal transmission. However, the challenge often lies in balancing rigidity with necessary flexibility for complex designs. This contradiction can lead to re-evaluations during the design phase, as some solutions may not fit the initial vision.
Tips: Consider using simulation software to visualize your design. This can save time and resources. Evaluate the material choices carefully; they can impact durability and performance. Remember, while smaller might be better, it should not sacrifice functionality. Check for potential overheating issues in densely populated layouts, as this can lead to reliability problems. Constantly reassess your designs as project requirements evolve.
Cost-Effectiveness and Production Efficiency of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs offer significant cost-effectiveness in the production process. Their design allows for accurate and repeatable manufacturing. This leads to reduced waste during production. Engineers can leverage automation to further streamline assembly. Fewer errors occur with rigid PCBs due to their stable structure. This results in lower labor costs and faster turnaround times.
Production efficiency is another advantage. Rigid PCBs enable complex circuit designs in a compact form. They support various components without compromising durability. This is crucial for devices requiring reliability over time. However, the initial design phase can be challenging. Engineers must consider thermal management and space constraints. Flaws in planning can lead to costly redesigns.
Another aspect to contemplate is material selection. While rigid PCBs are resilient, the materials used can impact costs. Premium materials may enhance performance but increase expenses. Balancing quality and cost is essential for maximizing returns. Overall, the journey to achieving cost-effective and efficient production with rigid PCBs involves thoughtful consideration and adaptation.
Thermal Management Advantages of Rigid PCB Solutions
Rigid PCB technology offers significant thermal management advantages. Unlike flexible alternatives, rigid PCBs provide superior heat dissipation. Their solid structure allows for effective thermal pathways. This is crucial for high-performance electronics that generate substantial heat.
With efficient thermal management, component longevity increases. Heat can lead to component failure if not properly managed. Rigid PCBs can integrate heatsinks or thermal vias effectively. This design flexibility is often overlooked but essential.
However, challenges exist. Design complexity can increase manufacturing costs. Temperature uniformity might not always be achieved. Engineers must consider material choices carefully. Balancing performance and expenses requires thoughtful reflection. Rigid PCBs present great potential, but not without hurdles.
Benefits of Using Rigid PCB Technology
Related Posts
-
Top Reasons to Choose PCB Rigid Flex for Your Next Electronics Project
-
Why Rigid PCB Is Essential for Modern Electronics Development?
-
The Future of PCB Manufacturing Innovations Transforming Electronics Industries
-
What is PCB Manufacturing and How Does it Impact Your Electronics Design
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using PCB Boards in Electronics Manufacturing
-

2026 How to Optimize Rigid Flex Circuit Design for Better Performance?
