2025 How to Choose the Right Flex Circuit Board for Your Projects
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electronic design, the selection of the right flex circuit board is crucial for optimizing performance and enhancing device functionality. Flex circuit boards, known for their lightweight and flexible designs, have been increasingly adopted across various industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices. According to a recent industry report by TechNavio, the global flex circuit board market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.87% from 2021 to 2025, highlighting the growing demand for these innovative solutions.
As we approach 2025, experts emphasize the importance of careful consideration when choosing flex circuit boards for specific applications. Dr. Martin Kline, a leading authority in flexible electronics, asserts, “The choice of flex circuit technology can greatly influence the overall efficiency and reliability of electronic devices. It’s essential to evaluate factors such as material properties, design complexity, and production capabilities.” This insight underlines the necessity for professionals to thoroughly understand the intricacies of flex circuit boards to make informed decisions that align with project requirements.
Furthermore, with advancements in manufacturing techniques and materials, projects now have access to enhanced options that can meet diverse performance needs. Decision-makers must remain informed about the latest technological trends and industry standards to ensure optimal functionality in their products. Armed with this knowledge, engineers can confidently navigate the myriad of choices available in the flex circuit board sector and select the most suitable solution for their projects.

Key Considerations for Selecting Flex Circuit Boards
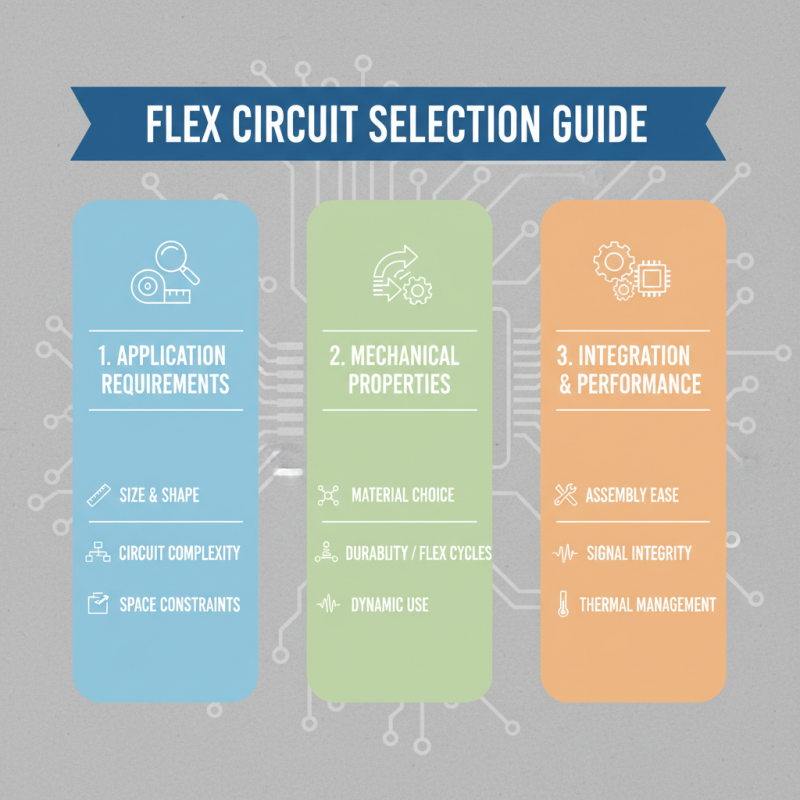
When selecting a flex circuit board for your projects, several key considerations should guide your decision-making process. First and foremost, the specific requirements of your application must be taken into account, including factors such as size, shape, and the complexity of the circuit design. Flex circuits offer distinct advantages in space-constrained environments, so understanding the dimensional limitations and how the circuit will be integrated into the overall assembly is crucial. Additionally, the mechanical properties of the materials chosen for the flex circuit can significantly impact its performance, especially in dynamic applications where bending and flexing will occur.
Another important aspect to consider is the electrical characteristics required for your project. This includes the number of layers, the type of conductors, and the dielectric materials used, all of which will affect signal integrity and overall performance. Engineers should evaluate thermal management as well, as flex circuits can experience different thermal conditions compared to rigid boards. By reviewing these parameters—structural integrity, electrical performance, and thermal considerations—you can make a more informed choice that aligns with the operational demands of your application.
Types of Flex Circuit Boards and Their Applications
Flex circuit boards, also known as flexible printed circuits (FPCs), come in various types, each designed to cater to specific applications in electronics. The most common types include single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer flex circuits. Single-sided flex circuits are ideal for simpler applications where space is a premium, providing a straightforward layout and design. These boards are typically used in everyday devices like mobile phones and wearables, where flexibility and lightweight construction are critical.
On the other hand, double-sided flex circuits offer more complex design options as they allow for components to be placed on both sides of the board. This type is advantageous in applications that require higher functionality within a compact space, such as medical devices and automotive electronic systems. Multi-layer flex circuits take this a step further, enabling intricate designs by stacking multiple layers of circuitry, which makes them suitable for high-performance applications like aerospace and advanced consumer electronics. The choice of flex circuit type will depend heavily on the specific needs of the project, including space constraints, required functionality, and budget considerations.
2025 How to Choose the Right Flex Circuit Board for Your Projects - Types of Flex Circuit Boards and Their Applications
| Type of Flex Circuit Board | Description | Common Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided Flex Circuit | A flex circuit with components on one side only. | Consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive sensors. | Cost-effective, lightweight, and flexible. | Limited component placement and routing options. |
| Double-Sided Flex Circuit | Flex circuit with components on both sides. | Smartphones, laptops, wearable technology. | More components can be placed, better routing flexibility. | Higher cost and complexity in manufacturing. |
| Multi-Layer Flex Circuit | Multiple flex layers bonded together. | High-density applications, aerospace, specialized medical devices. | Supports complex designs with multiple circuits. | Higher fabrication cost and potential thermal issues. |
| Rigid-Flex Circuit | Combination of flexible and rigid circuit boards. | Telecommunications, aerospace, automotive. | Space-saving and enhanced durability. | More complex design and costlier to produce. |
| Impedance Control Flex Circuit | Designed for high-frequency applications with controlled impedance. | RFID technology, telecommunications, high-speed digital circuits. | Optimizes signal integrity and reduces losses. | Requires precise manufacturing processes. |
Material Selection for Optimal Performance in Flex Circuits
When selecting materials for flex circuit boards, the choice significantly impacts performance, durability, and application suitability. According to industry reports, polyimide films lead the market due to their exceptional thermal stability and inherent flexibility, making them ideal for applications ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace. Notably, polyimide exhibits a high dielectric strength, with values often exceeding 500V/mil, allowing for reliable performance in high-frequency applications. In fact, a recent study indicated that flex circuits utilizing polyimide can maintain structural integrity even at temperatures above 200°C, which is critical for long-term reliability in demanding environments.
In addition to polyimide, selecting the right conductor material is vital. Copper remains the most widely used conductive material due to its excellent electrical conductivity, with a conductivity rating of around 58 MS/m. However, alternative materials like silver and aluminum are emerging for specific applications, particularly where weight reduction is essential. Industry research suggests that using silver in high-performance applications can enhance signal integrity, although the cost factor must be weighed against performance benefits. To ensure optimal functionality, engineers must also consider factors such as adhesive compatibility, layer thickness, and the intended environmental conditions during the material selection phase of flex circuit design.
Manufacturing Processes and Their Impact on Circuit Quality
When selecting the right flex circuit board for your projects, understanding the various manufacturing processes is crucial as they directly impact the quality and performance of the final product. The most common methods for fabricating flex circuit boards include subtractive, additive, and semi-additive processes. Each of these techniques has its own unique advantages and limitations that can affect the circuit’s dimensional accuracy, layer thickness, and overall durability. For instance, subtractive processes, typically used for traditional printed circuit boards, can efficiently produce complex designs but may result in excess material waste. In contrast, additive processes allow for greater flexibility in design and can enhance performance, particularly for high-density applications.
Furthermore, the choice of materials during the manufacturing phase significantly influences circuit quality. The substrate materials, such as polyimide and polyester, offer varying levels of thermal stability, dielectric strength, and flexibility. A proper understanding of these materials, coupled with the selected manufacturing process, ensures that the final circuit board meets the required specifications and can endure the intended application environment. Detailed attention to these factors during the pre-fabrication phase ultimately determines the reliability and lifespan of the flex circuit, making it imperative to align manufacturing choices with project needs.
2025 Flex Circuit Board Quality Metrics
Cost Analysis: Balancing Budget and Flex Circuit Requirements
In today's rapidly evolving electronics landscape, choosing the appropriate flex circuit board requires a meticulous balancing act between cost and performance. Recent industry analysis indicates that the global flexible circuit market is projected to exceed $21 billion by 2025, reflecting a robust demand driven by technological advancements in sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices. The key to optimizing your project’s budget lies in understanding the various factors that contribute to the costs of flex circuits, including material selection, manufacturing processes, and design complexity.
Material choice plays a pivotal role in determining not only the functionality and reliability of flex circuits but also their cost. For instance, while polyimide is a popular choice for its thermal stability and flexibility, alternative materials like polyester can offer significant savings for less demanding applications. According to a recent report by Smithers Pira, the average cost of basic polyimide substrates can range from $0.10 to $0.50 per square inch, whereas polyester options may be priced as low as $0.05 per square inch.
Additionally, the integration of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as roll-to-roll processing, can further optimize production efficiency, reducing costs associated with labor and material waste. Understanding these aspects will ensure that designers not only meet the technical requirements of their projects but also achieve a favorable return on investment.
As with any design project, careful planning can alleviate potential financial challenges. Early-stage prototyping and simulation can help identify necessary adjustments to minimize waste. Furthermore, collaborating with engineers who specialize in flexible circuits can provide insights into cost-effective design practices. The ultimate objective is to create a durable and functional flex circuit while adhering to budget constraints, thus allowing for innovation without compromising on quality.
Related Posts
-
Understanding the Importance of Flexible Printed Circuits in Modern Electronics
-
Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Circuit Board Design in 2024 and Beyond
-

Revolutionizing Circuit Board Manufacturing: Innovative Techniques for Efficient Production
-
What is Circuit Board Design and How to Get Started with It
-
Top 7 Most Innovative Techniques in Circuit Board Production You Need to Know
-

What is Circuit Board Manufacturing? A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
