10 Essential Tips for Understanding Circuit Boards and Their Functionality
Understanding circuit boards and their functionality is essential for anyone venturing into the world of electronics, whether you are a hobbyist, a student, or a professional in the field. Circuit boards are the backbone of most electronic devices, serving as a platform for the interconnection and functioning of various components. With ever-evolving technology, grasping the nuances of circuit board design and operation can empower individuals to troubleshoot issues, innovate designs, and enhance their understanding of how electronic systems work as a whole.
In this guide, we will explore ten essential tips that will demystify circuit boards for you. From recognizing the different types of circuit boards to understanding the role of various components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, each tip serves as a stepping stone towards mastering the complexities of these critical pieces of technology. By building a foundational knowledge of circuit board functionality, you will be better equipped to engage with the electronic devices that shape our modern world and unlock your potential for creativity and problem-solving in electronics.
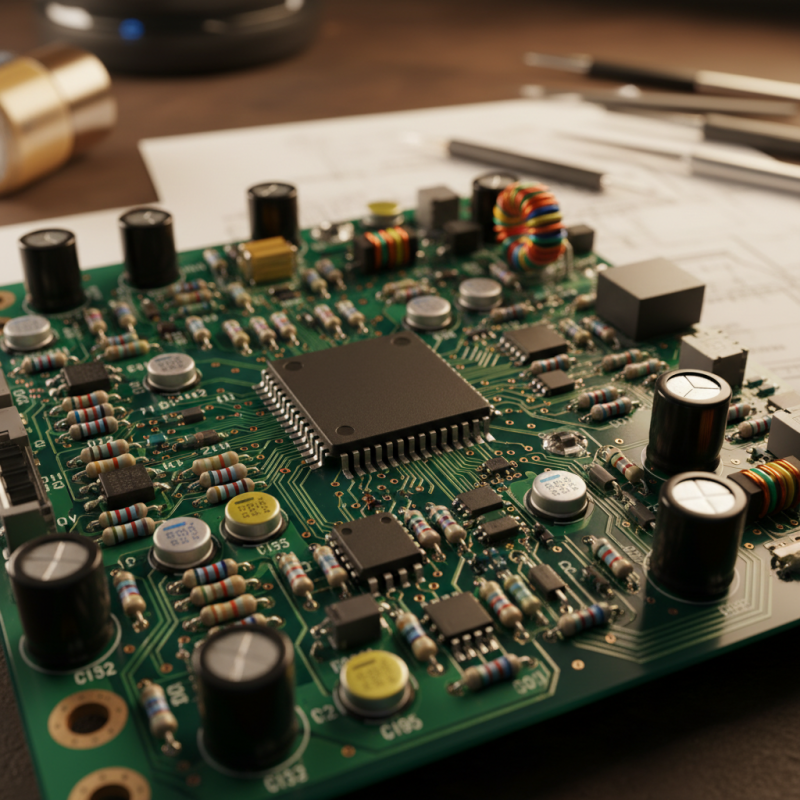
Understanding the Basic Components of Circuit Boards
Circuit boards are the backbone of modern electronic devices, consisting of various essential components that work together to facilitate functionality. Understanding these basic components is crucial for anyone interested in electronics. The most fundamental part of a circuit board is the substrate, typically made of fiberglass or plastic, which provides the physical structure and insulation required for the electrical pathways. On this substrate, copper traces serve as the pathways for electrical current, connecting different components and allowing them to communicate.
Other vital elements on a circuit board include resistors, capacitors, diodes, and transistors. Resistors control the flow of electric current, ensuring that components receive the appropriate amount of power. Capacitors store and release energy as needed, smoothening out voltage fluctuations. Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, protecting sensitive components from potential damage. Transistors act as switches or amplifiers, playing a key role in signal processing. By understanding these components, enthusiasts can troubleshoot issues, design custom circuits, or enhance their knowledge of how devices operate.
The Role of Conductors and Insulators in Circuit Functionality
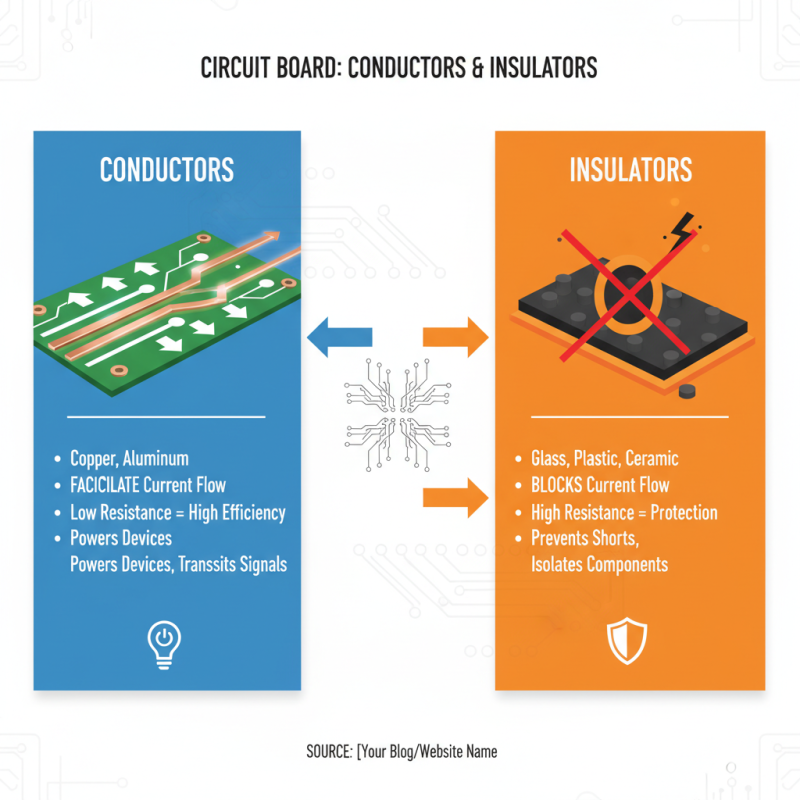
The functionality of circuit boards heavily relies on the roles played by conductors and insulators within the circuitry. Conductors, typically made of materials like copper or aluminum, facilitate the flow of electrical current throughout the circuit. Their primary function is to provide a pathway for electrons to move, enabling the circuit to perform actions such as powering devices or transmitting signals. The efficiency of a conductor is determined by its resistance; materials with lower resistance allow for better conductivity, reducing energy loss and heat generation.
On the other hand, insulators play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and safety of circuit boards. Made from materials like rubber, glass, or certain plastics, insulators are designed to prevent the unwanted flow of electricity. They ensure that current travels only along designated paths, thereby reducing the risk of short circuits and electrical failures. Proper insulation is essential, not only to protect the components on the board but also to safeguard users from electric shock. Understanding the interplay between conductors and insulators is vital for anyone looking to grasp the fundamental principles of circuit functionality.
How to Read a Circuit Diagram Effectively
Reading a circuit diagram effectively is a crucial skill for anyone looking to understand the functionality of circuit boards. A circuit diagram, or schematic, provides a visual representation of an electrical system, detailing the connections and components involved. To begin, familiarize yourself with the basic symbols used in circuit diagrams, such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes. Each symbol has a specific meaning and understanding these can help you decipher the role of each component in the circuit.
Once you are comfortable with the symbols, practice identifying how components are interconnected. Pay attention to the lines representing wires; they can indicate direct connections or junction points where multiple components converge. It’s also essential to follow the flow of electricity, which is typically represented by arrows in the diagram. This will help you grasp how signals move through the circuit and how various components interact with one another. By systematically analyzing a circuit diagram, you can gain deeper insight into the functionality of the corresponding circuit board, ultimately enhancing your electronic design and troubleshooting skills.
Common Types of Circuit Boards and Their Applications
Circuit boards are integral components in a myriad of electronic devices, ranging from consumer electronics to advanced industrial systems. Primarily, there are three common types of circuit boards: single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards. Single-sided boards consist of one layer of conductive material, making them simpler and more cost-effective, typically used in basic devices like calculators and toys. According to industry reports, single-sided boards dominate the market for entry-level applications, holding approximately 35% of the circuit board production by volume.
In contrast, double-sided circuit boards feature conductive pathways on both sides, enabling more complex layouts and higher device functionality, thus applicable in devices like smartphones and computers. The latest analyses indicate that the double-sided board segment contributes to around 40% of the overall circuit board market, reflecting the increasing demand for compact and efficient electronic solutions. Lastly, multi-layer circuit boards, which can have up to 20 layers, are essential for high-density applications such as servers and medical equipment, with approximately 25% of the market share. The trend towards miniaturization and increased functionality drives the growth of multi-layer boards, which are increasingly utilized in sophisticated electronic products.
Common Types of Circuit Boards and Their Applications
Troubleshooting Circuit Board Issues: Tips and Techniques
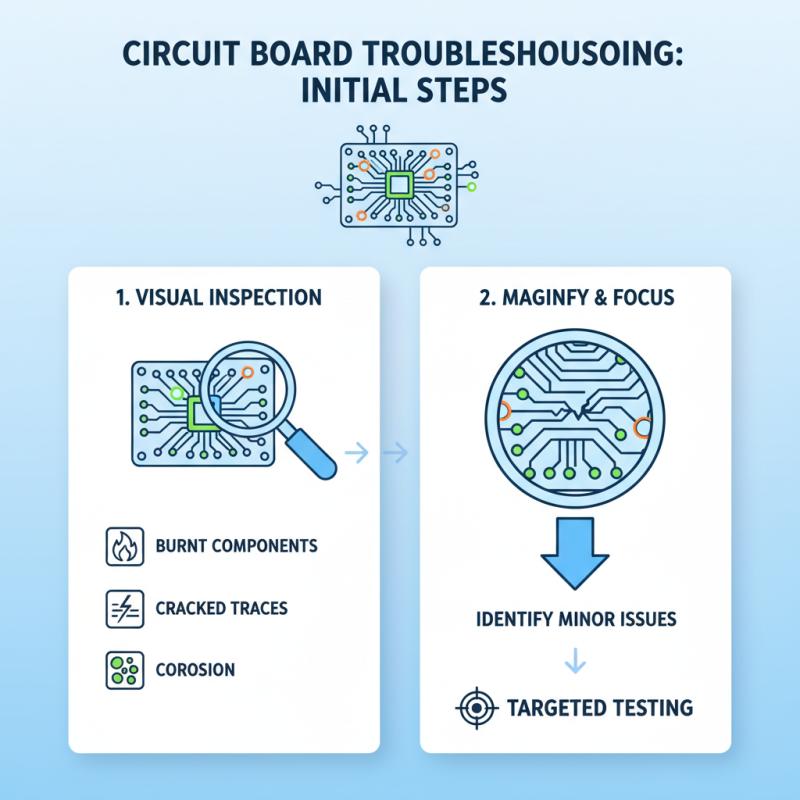
Troubleshooting circuit board issues can be a complex task, but with the right approach and techniques, many problems can be diagnosed and resolved effectively. First, it's crucial to visually inspect the circuit board for obvious signs of damage, such as burnt components, cracked traces, or corrosion. Using a magnifying glass can help identify minute issues that are not immediately visible to the naked eye. This preliminary inspection allows for a more targeted troubleshooting process, focusing on specific areas that may need further testing.
After the initial inspection, utilizing a multimeter to check for continuity and measure voltage levels is essential. This tool can help verify whether current is flowing through the intended pathways and assist in pinpointing malfunctions in components or connections. If a specific component is suspect, it can often be tested in-circuit or removed for separate testing. Moreover, employing thermal imaging can reveal overheating components that may be contributing to circuit failure. Engaging with these techniques methodically can lead to more precise diagnoses and ultimately restore the circuit board’s functionality efficiently.
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Circuit Board Manufacturing: Innovative Techniques for Efficient Production
-
What is Circuit Board Design and How to Get Started with It
-

What is Circuit Board Manufacturing? A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
-
Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Circuit Board Design in 2024 and Beyond
-
The Future of PCB Manufacturing Innovations Transforming Electronics Industries
-
Top 7 Most Innovative Techniques in Circuit Board Production You Need to Know
