What is a Flexible PCB Board and How is it Used?
Flexible PCB boards are revolutionizing the electronics industry. Their unique structure allows for adaptability in various devices. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global flexible PCB market is expected to reach $29.8 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 13.8%. This trend shows that flexible PCB boards are not just a niche product; they are becoming essential.
These boards can bend and fit in tight spaces, which is crucial for today's compact gadgets. The demand is particularly high in sectors like consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices. For instance, smartphones and wearables rely heavily on flexible PCB technology for enhanced functionality. However, despite their advantages, issues like manufacturing complexities and cost can arise.
As more companies adopt flexible PCB boards, the industry faces challenges. It is vital to address these hurdles to harness their full potential. Balancing innovation with practicality remains an ongoing concern. The journey to optimize flexible PCB technology is still evolving and demands careful consideration.

Definition and Characteristics of Flexible PCB Boards
Flexible PCB boards, commonly known as flexible printed circuits, are essential in modern electronics. They consist of a thin layer of insulating material, often polyimide or polyester, that is flexible and lightweight. This allows them to bend and twist, making them ideal for compact devices where space is at a premium. Their design enables them to fit into complex shapes, a significant advantage in smartphones, wearables, and medical devices.
These boards have unique characteristics. They can withstand heat and have excellent electrical characteristics. Flexible PCBs also reduce the overall weight of devices. However, they can be challenging to manufacture. Consistency in thickness is crucial for performance, yet it can often fluctuate. This inconsistency may lead to malfunctioning electronics. Additionally, the delicate nature of these boards can make them more susceptible to damage during assembly, requiring careful handling and inspection.
In use, flexible PCB boards demonstrate remarkable versatility. They are found in automotive applications, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment. However, their complexity can pose challenges in design. As engineers push for innovation, they must consider the potential for failure. The balance between flexibility and reliability is a critical aspect that requires ongoing reflection and refinement in the industry.
Applications of Flexible PCBs in Consumer Electronics

Flexible PCBs, or printed circuit boards, are revolutionizing consumer electronics. They offer distinct advantages in compactness and versatility. Research indicates that the global flexible PCB market is expected to reach $30 billion by 2025. This growth is largely driven by increasing demand for consumer electronics. Flexible PCBs are lightweight and can be molded into various shapes, making them ideal for products like smartphones, wearables, and medical devices.
In consumer electronics, applications are vast. For instance, flexible PCBs are commonly used in smartphones for their compact design. They enable multilayer configurations that support complex functions in a limited space. Wearable devices also benefit significantly. The flexibility of these PCBs allows for better fit and comfort in devices like fitness trackers. Moreover, medical devices are increasingly adopting flexible PCBs for their enhanced reliability and functionality. This trend suggests an ongoing shift towards miniaturization and multi-functionality in technology.
Yet, challenges persist. Production can be more complex than traditional rigid boards. Yield rates need improvement to reduce costs. Additionally, as devices get thinner, material durability is crucial. If a flexible PCB fails, it can compromise the entire device. These issues highlight the need for ongoing research and innovation in this field.
Market Trends and Growth Projections for Flexible PCB Industry
The flexible PCB industry is experiencing rapid growth, driven by technological advancements. In 2022, the global market size was valued at approximately $25 billion. It is projected to reach around $45 billion by 2028. This growth, estimated at a CAGR of 10% from 2023 to 2028, highlights increasing demand in sectors like consumer electronics, automotive, and healthcare.
As devices become smaller and more complex, flexible PCBs are essential. They allow for tighter designs without compromising performance. For instance, flexible PCBs are crucial in smartphone manufacturing and wearable technology. These applications demand durability and compactness. Market analysts note a shift towards more efficient production processes, but challenges remain. Manufacturers need to address high material costs and ensure quality control.
Regional trends show significant growth in Asia-Pacific, particularly in China and India. Companies in these regions are ramping up production to meet local and global demands. However, issues like skilled labor shortages can hinder progress. Companies must adapt and invest in training to maintain competitive advantages. While the future looks promising, the industry must navigate these hurdles carefully.
Manufacturing Processes and Techniques for Flexible PCBs
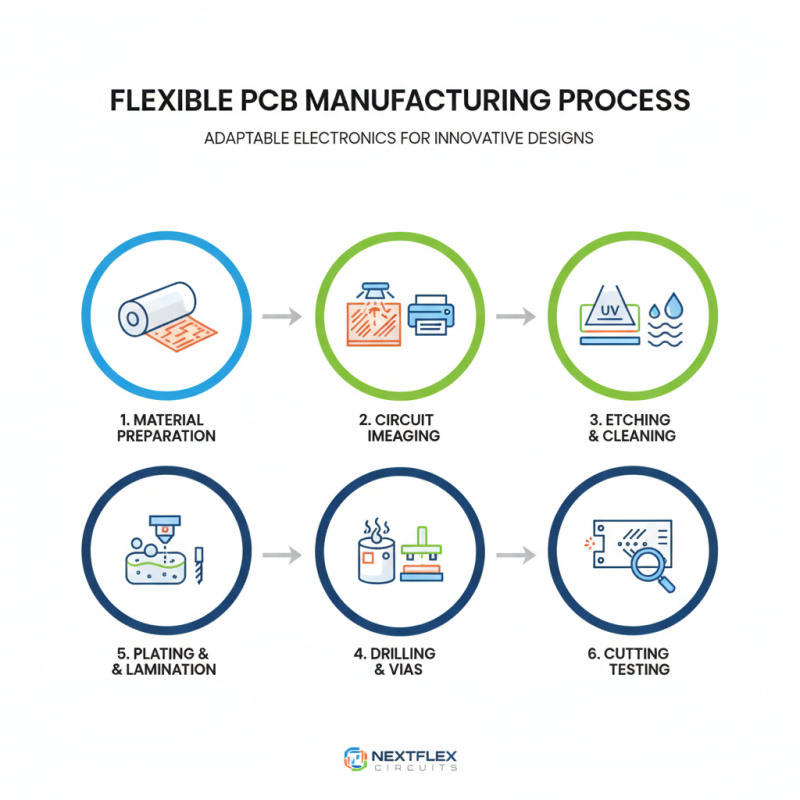
Flexible PCBs are unique in their ability to bend and fold. This adaptation allows them to fit complex shapes in various devices. The manufacturing process leading to these boards involves several intricate steps.
The initial stage includes designing the circuit layout. Designers often use specialized software to ensure precision. Next, a thin substrate material is selected. Polyimide or polyester are common choices. These materials provide the necessary flexibility. Afterward, the printed circuit patterns are etched onto the substrate. This process requires careful attention to detail. Mistakes in this stage can lead to future failures.
Then, layers may be added to enhance performance or connectivity. Adhesives secure these layers together. A key challenge is ensuring that all layers are aligned properly. Proper alignment is essential to prevent circuit faults. Lastly, the finished flexible PCB is tested. This step helps identify any manufacturing flaws before mass production. Each of these steps is vital, yet often overlooked in discussions about flexible PCB technology. Attention to detail in manufacturing affects the final product's reliability and performance.
Advantages and Challenges of Using Flexible PCBs in Design
Flexible PCBs, or printed circuit boards, offer unique advantages in design but come with certain challenges. Their ability to bend and twist makes them ideal for compact devices. These boards can fit into tight spaces. They are often used in smartphones, wearables, and medical devices. This flexibility enables innovative product designs.
However, there are drawbacks to consider. Manufacturing flexible PCBs can be more complex. They often require specialized techniques, which may increase costs. Repairing these boards is also challenging. Once damaged, they are often difficult to fix without replacing the entire unit. Designers must weigh these factors carefully.
Tips: Choose the right materials for flexibility. They should withstand bending and twisting. Also, consider the environment. Humidity and temperature can affect performance. Always test designs under real-world conditions. A small oversight may lead to significant problems later on. Be mindful of production timelines too. They can impact project budgets and schedules.
Advantages and Challenges of Using Flexible PCBs
Related Posts
-
Understanding Rigid Flex PCB Applications and Advantages in Electronics
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Flexible PCBs for Your Project
-
Top Benefits of Using Printed PCB for Your Electronic Projects
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Flex PCB Board for Your Project
-

How to Choose the Right Flex PCB Board for Your Project Needs
-
What is Circuit Board Design and How to Get Started with It
