What is a PCB Circuit? Understanding the Basics and Applications Explained
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics, the significance of a PCB circuit cannot be overstated. As the backbone of virtually all electronic devices, printed circuit boards (PCBs) facilitate the complex interconnections between various components, enabling them to function harmoniously. According to Dr. Emily Roberts, a renowned expert in electronic engineering, "Understanding the fundamentals of PCB circuit design is essential for anyone looking to innovate in the tech industry." Her insight underscores the critical role that PCB circuits play not only in traditional applications but also in advancing emerging technologies.
The basic principles of PCB circuits involve layers of conductive pathways and insulating materials that serve to connect and support electronic components. This intricate design allows engineers to create compact and efficient configurations, significantly impacting the size and performance of devices. As we delve into the various applications of PCB circuits, it becomes clear that their versatility spans from consumer electronics to aerospace and automotive industries, highlighting their foundational role in the technology that shapes our daily lives. Through this exploration, we aim to deepen our understanding of PCBs and their importance in modern electronics.
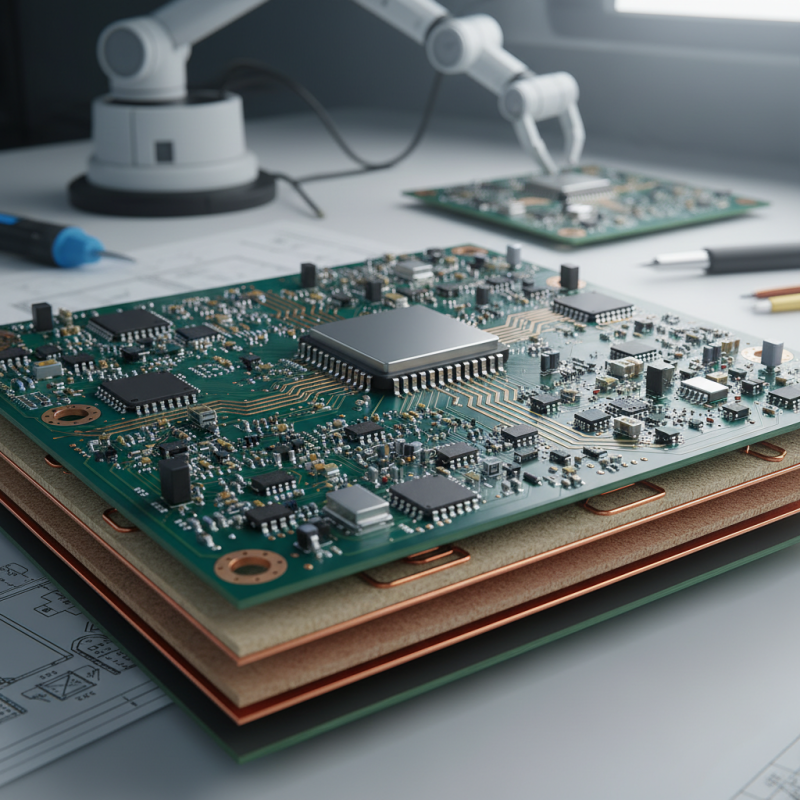
What is a PCB Circuit?
A PCB circuit, or printed circuit board circuit, is a fundamental component in electronic devices, serving as the backbone that connects different electronic components. PCBs are made from a non-conductive material, usually fiberglass or plastic, with conductive pathways etched onto their surface. These pathways, or traces, facilitate the flow of electrical signals between various components like resistors, capacitors, and microcontrollers, thereby enabling the device to function properly.
When designing or working with PCB circuits, it's essential to keep in mind several tips. First, ensure that your layout is clear and intuitive, minimizing the possibility of errors during production. Utilizing software tools for PCB design can greatly aid in visualizing the circuit and identifying potential issues before fabrication. Additionally, consider the thermal management of your circuit; overheating can damage components. Strategically placing components and incorporating thermal vias can help maintain an optimal operating temperature.
Understanding the fundamentals of PCB circuits not only aids in efficient electronic design but also opens up numerous applications across industries, from consumer electronics to automotive technology. As technology continuously evolves, the versatility and importance of PCBs remain critical in crafting the devices of tomorrow.
PCB Circuit Applications and Revenue Growth
This bar chart illustrates the revenue generated by different applications of PCB circuits. The consumer electronics sector leads with significant revenue, followed by automotive and telecommunications. Understanding these applications is crucial for grasping the importance of PCBs in various industries.
Components of a PCB Circuit
A printed circuit board (PCB) is a fundamental component in modern electronics, serving as the backbone for circuit connections. Understanding the basic components of a PCB is essential for anyone involved in electronics design or manufacturing. At its core, a PCB consists of several key elements, including conductive pathways, substrates, and various electronic components.
The conductive pathways, typically made of copper, create a network through which electrical signals can travel. These traces are meticulously designed to connect different components placed on the board, ensuring that each part can communicate effectively. The substrate, usually composed of fiberglass or plastic, provides structural support and electrical insulation, allowing the circuit to function without interference.
In addition to the pathways and substrate, a PCB incorporates several electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits. Each component plays a specific role in the circuit, from regulating power flow to processing signals. Understanding how these components interact on a PCB is crucial for troubleshooting and optimizing electronic designs, making it essential knowledge for engineers and hobbyists alike.
What is a PCB Circuit? Understanding the Basics and Applications Explained - Components of a PCB Circuit
| Component | Function | Common Materials | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistors | Limit current flow and divide voltages | Carbon film, Metal film | Power supplies, Signal conditioning |
| Capacitors | Store and release electrical energy | Ceramic, Electrolytic | Power smoothing, RF filter |
| Inductors | Store energy in a magnetic field | Copper wire, Ferrite core | Power supplies, Signal filtering |
| Diodes | Allow current flow in one direction | Silicon, Germanium | Rectification, Signal modulation |
| Transistors | Amplify and switch electronic signals | Silicon, Gallium arsenide | Oscillators, Digital circuits |
| Connectors | Join electrical circuits | Plastic, Metal | Interconnecting devices, PCB-to-PCB connections |
Manufacturing Process of PCB Circuits
The manufacturing process of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) circuits is a critical aspect of electronics production that requires precision and meticulous attention to detail. The process typically begins with the design phase, where engineers use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to create layouts. According to industry reports, the global PCB market is projected to reach approximately $80 billion by 2025, demonstrating the increasing demand for these essential components in various applications ranging from consumer electronics to aerospace.
Once the design is finalized, the actual manufacturing kicks off with the creation of the PCB substrate, usually made from materials like FR4 or CEM1. This substrate is then coated with a layer of copper, which is selectively etched away to form the circuit pathways. The etching process, often involving chemical solutions or laser technologies, ensures that the conductive paths are precise and reliable. Recent advancements have enabled manufacturers to produce PCBs with higher density and more complex layouts, in response to the growing trend of miniaturization in electronics.
After etching, the next steps include drilling holes for components and plating them with a conductive layer to create connections. The final stages involve applying solder mask and silkscreen for protection and legibility, followed by testing for quality assurance. With increased automation and the adoption of smart manufacturing practices, efficiency in PCB production continues to improve, with reports indicating a reduction in lead times and production costs while enhancing the overall quality of the circuits. This evolution in manufacturing processes is crucial as industries seek to integrate more advanced technologies into their products, thus driving the innovation in PCB applications.
Common Applications of PCB Circuits
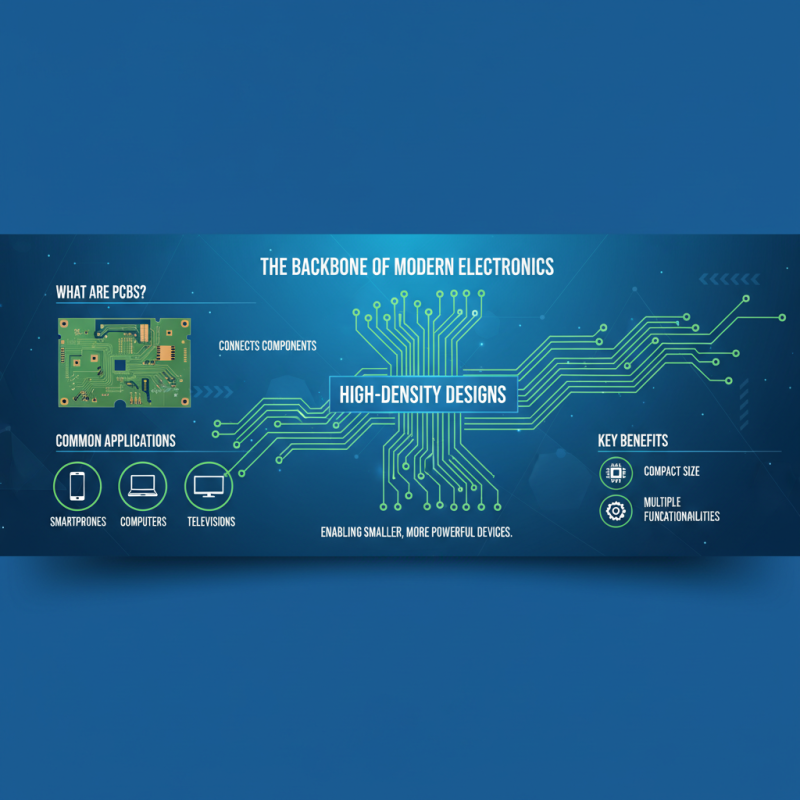
PCB circuits, or printed circuit boards, are pivotal in modern electronics, serving as the backbone for a multitude of devices. One of the most common applications of PCB circuits is in consumer electronics such as smartphones, computers, and televisions. These devices rely on intricate PCB designs to connect various components like processors, memory, and displays. The compact nature of PCBs allows for high-density circuit arrangements, making it possible to incorporate numerous functionalities into smaller devices without compromising performance.
Another significant application of PCB circuits can be found in industrial machinery and equipment. In this sector, PCBs are essential for controlling various operations, including automation processes, monitoring systems, and power management. They ensure reliability and precision in environments that require constant operation and can withstand harsh conditions. Additionally, PCBs are used in medical devices, where they play a crucial role in diagnostics and patient monitoring equipment. By enabling accurate data processing and signal transmission, PCBs enhance the functionality and efficiency of medical technologies, ultimately contributing to better patient care.
Future Trends in PCB Technology

The future of PCB technology is set to be shaped by advancements in automation, miniaturization, and sustainability. As the demand for more compact and efficient electronic devices continues to rise, PCBs are evolving rapidly. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global printed circuit board market is expected to reach $75.6 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 4.2%. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of IoT devices and smart applications across various sectors, including automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics.
One notable trend in PCB technology is the integration of flexible and rigid-flex circuits, which allow for a more versatile design in applications ranging from medical devices to aerospace components. Furthermore, the development of advanced materials, such as high-frequency laminates and environmentally friendly substrates, is making PCBs more efficient and resilient. Research from IPC indicates that manufacturers are increasingly investing in sustainable practices, with over 60% of surveyed companies recognizing the importance of eco-friendly processes in their production systems. This shift not only addresses regulatory concerns but also caters to an environmentally conscious market, positioning PCB technology for a sustainable future.
Related Posts
-
Understanding the Latest Innovations in PCB Manufacturing for Modern Electronics
-
Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Circuit Board Design in 2024 and Beyond
-

Revolutionizing Circuit Board Manufacturing: Innovative Techniques for Efficient Production
-
The Future of PCB Manufacturing Innovations Transforming Electronics Industries
-
Understanding PCB Production: Essential Insights for Future Electronics Innovators
-
What is Circuit Board Design and How to Get Started with It
