Understanding Rigid Flex PCB Applications and Advantages in Electronics
Rigid flex PCBs are becoming increasingly prevalent in the electronics industry. They combine the benefits of rigid and flexible PCB technologies. According to a report by the IPC, the market for rigid flex PCBs is expected to grow by over 10% annually. This growth shows their importance in modern electronic devices.
In applications like smartphones and medical devices, rigid flex PCBs provide design flexibility. They allow for compact layouts in limited spaces. This technology enables manufacturers to create thinner, lighter products, which is a significant advantage. However, challenges remain in their manufacturing processes. For instance, the complexity can lead to higher costs.
The incorporation of rigid flex PCB can present obstacles in standardization and testing. These issues can impact overall product quality. Companies must evaluate these trade-offs carefully. The advantages are clear, but they come with their own set of challenges. In the fast-evolving electronics landscape, addressing these issues is crucial for successful integration.
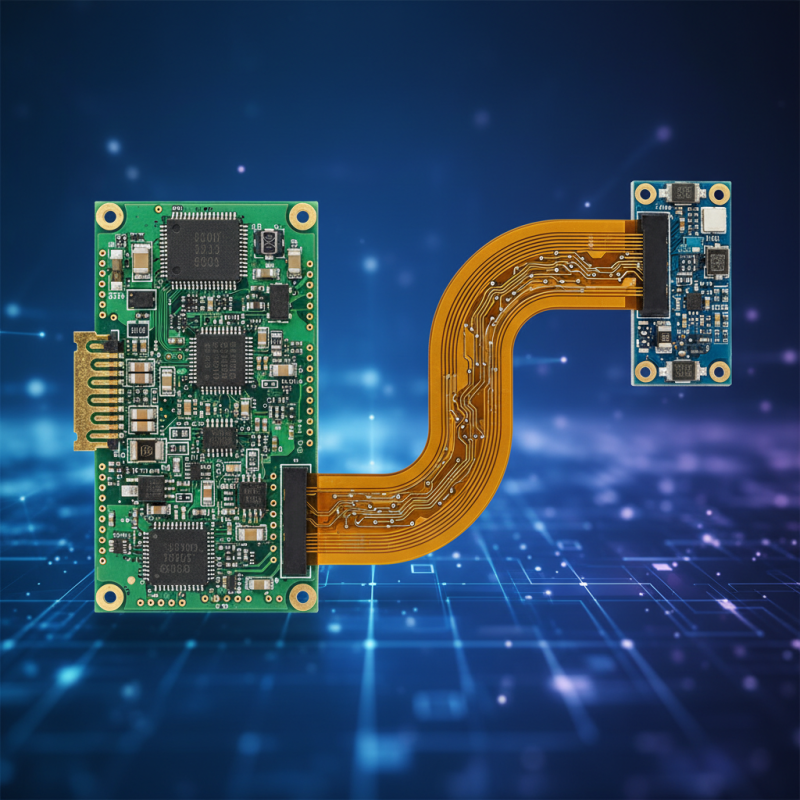
Overview of Rigid Flex PCBs in Modern Electronics
Rigid flex PCBs have gained traction in modern electronics due to their unique structure. Unlike traditional PCBs, they combine rigid and flexible materials. This design offers more versatility and efficiency for various applications. According to a recent industry report, the rigid-flex PCB market is expected to grow by 10% annually, reaching over $15 billion by 2025.
In consumer electronics, rigid flex PCBs are increasingly used in smartphones and wearable devices. They allow for compact designs without sacrificing performance. Flexible circuits can navigate tight spaces, reducing assembly time. A study suggested that solutions using rigid flex technology can decrease total weight by 30%. However, challenges remain. Manufacturing these boards can be complex and costly. It requires advanced techniques to ensure reliability and performance.
Health and medical devices also benefit from rigid flex designs. They can accommodate several functions in a single board. Importantly, this can lead to smaller, more efficient devices. Researchers noted that 40% of medical innovations are using such technologies. Still, issues like thermal management and circuit durability need addressing. Ongoing R&D may help solve these concerns.
Understanding Rigid Flex PCB Applications and Advantages in Electronics
| Application | Advantages | Typical Industries | Design Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Space-saving, lightweight | Home appliances, smartphones | High |
| Medical Devices | Reliable performance, high durability | Diagnostic equipment | Moderate |
| Automotive Systems | Enhanced thermal management | Electric vehicles, infotainment | High |
| Aerospace Applications | High reliability under extreme conditions | Navigation systems | Moderate |
| Telecommunications | Improved signal integrity | Networking devices | High |
Key Applications of Rigid Flex PCBs Across Various Industries
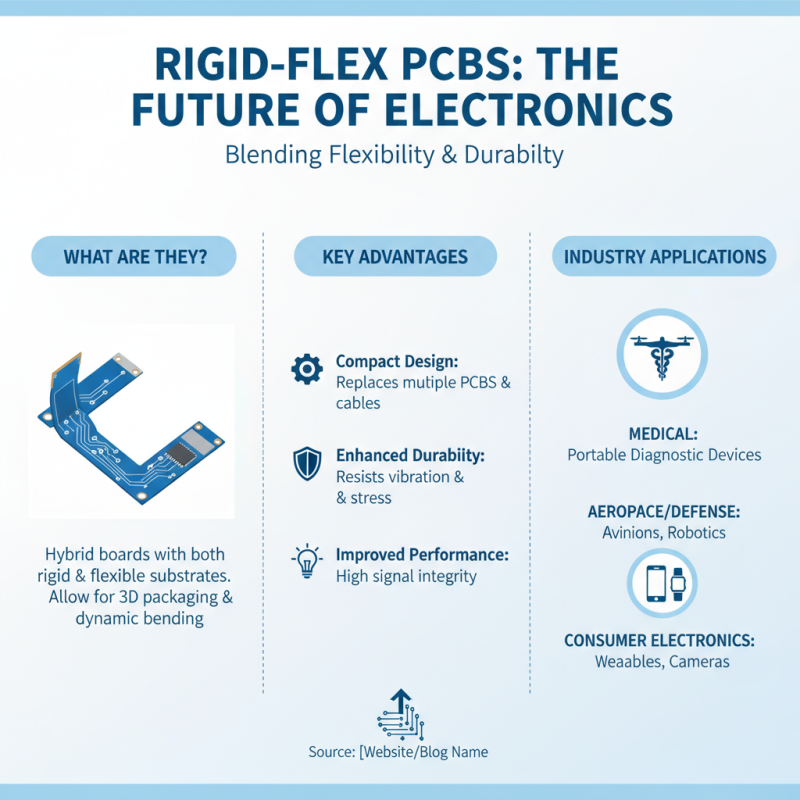
Rigid flex PCBs are gaining traction in various industries due to their unique blend of flexibility and rigidity. These boards are pivotal in applications that require compact designs and durable performance. In the medical field, for instance, they are used in portable diagnostic devices. The ability to fit complex circuitry in tight spaces is invaluable. These devices must withstand frequent handling and environmental challenges.
In aerospace and automotive sectors, rigid flex PCBs provide lightweight solutions that reduce overall system weight. This is crucial for improving fuel efficiency and performance. Additionally, their ability to endure the rigors of varying temperatures makes them ideal for electronic control units. Designers often face challenges in achieving a balance between flexibility and reliability. Several iterations may be necessary to find the right configuration.
Consumer electronics also benefit significantly from rigid flex technology. Smartphones and wearables utilize them for multi-layer functionalities. While these designs enhance usability, they can sometimes lead to production complexities. The integration of more features can complicate assembly. Continuous innovation is vital to address these hurdles effectively. Rigid flex PCBs present exciting opportunities alongside their challenges, driving progress in electronics design.
Advantages of Rigid Flex PCB Technology Over Traditional PCBs
Rigid flex PCB technology is gaining traction in various electronic applications. Its ability to bend and flex without breaking presents significant advantages over traditional PCBs. Reports indicate that the market for rigid flex PCBs is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10% through 2025, driven by the demand for compact, lightweight designs. This technology offers a reduction in the number of interconnects needed, which can decrease assembly time and costs.
One of the main benefits is the durability of rigid flex PCBs. They can withstand harsh conditions, making them ideal for use in aerospace and medical devices. For instance, a study highlighted that rigid flex designs can endure over 2000 flex cycles without failure. In contrast, traditional PCBs often face limitations with flexibility and mechanical stress, leading to higher failure rates. Some manufacturers still struggle with the transition to this modern technology, particularly in understanding the complexities of design and production.
Moreover, the integration of multiple functionalities into a single board can minimize space in intricate electronic systems. However, this complexity can also lead to potential design challenges. Engineers may need to rethink their approaches when developing with rigid flex technology. Balancing performance and reliability remains a key hurdle for many in the industry.
Design Considerations for Rigid Flex PCB Integration
When integrating rigid flex PCBs into electronic designs, several considerations arise. The unique architecture of these PCBs combines both rigid and flexible materials. This characteristic allows for complex shapes and space-efficient designs. Designers must carefully assess the mechanical properties of the materials used. The bending radius is a key factor that impacts reliability. If not considered properly, it can lead to failures in the circuits.
Thermal management is another crucial aspect. Rigid flex PCBs often deal with heat dissipation challenges. High-performance components generate significant heat. Designers should ensure adequate heat sinking and ventilation within their layouts. In some cases, thermal expansion mismatches can cause stress and warping. Regular testing and iterations might be necessary to achieve the desired results.
Finally, through-hole and surface mount technology must be compatible with the design. Ensuring proper alignment during assembly is vital. Misalignment can introduce complications. A meticulous review of the layout is essential before production. These challenges serve as learning opportunities for engineers, pushing them to refine their techniques further.
Future Trends in Rigid Flex PCB Development and Usage
The landscape of rigid flex PCB technology is evolving rapidly. Future trends indicate significant growth in application sectors such as wearable devices, automotive, and aerospace. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the rigid flex PCB market is projected to reach $10.2 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.4%. This indicates robust opportunities for manufacturers and designers alike.
Wearable devices are leading this charge. Their compact designs require reliable flex circuits. Rigid flex PCBs provide the ideal solution to meet these demands. They offer durability while maintaining lightweight characteristics. The automotive sector is also embracing this technology. Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and electric vehicles boost the need for efficient electronic designs. Yet, the implementation can sometimes lead to challenges in cost management and manufacturing complexity.
Tip: Always consider the long-term reliability of your design. In this evolving market, flexibility is essential. The ability to adapt to changes can lead to more sustainable decisions. Investing in better fabrication techniques may seem costly, but it pays off in the long run. Simplifying complex assemblies could mitigate potential risks. Engage with your engineering team early on to align goals and expectations.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Flex PCB Board for Your Project
-

How to Choose the Right Flex PCB Board for Your Project Needs
-
Exploring the Future of Electronics: How Flexible Printed Circuit Boards Will Revolutionize device Design in 2024
-
Top 7 Most Innovative Techniques in Circuit Board Production You Need to Know
-
Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Circuit Board Design in 2024 and Beyond
-

Top 10 Circuit Board Design Tips for Beginners and Experts
