What is Rigid Flex Rigid PCB and How it Benefits Modern Electronics
In the rapidly evolving landscape of modern electronics, the demand for innovative manufacturing techniques is at an all-time high. One such advancement is the rigid flex rigid PCB, a hybrid printed circuit board that combines the benefits of both rigid and flexible PCB technologies. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global flexible printed circuit board market is projected to reach USD 40.07 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 10.14% from 2020. This increasing market demand is significantly influenced by the growing prevalence of wearable devices, IoT applications, and the requirement for compact electronic solutions.
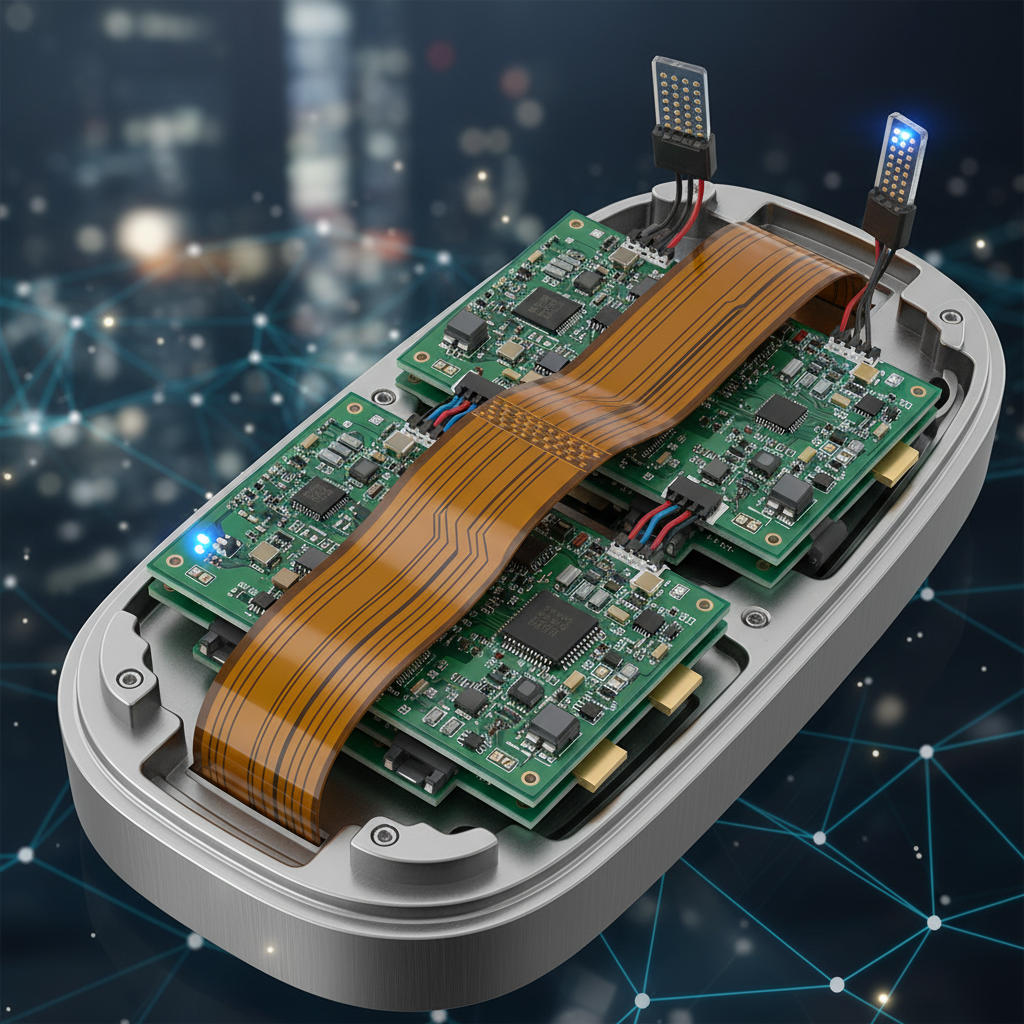
Rigid flex rigid PCBs provide a unique advantage by minimizing the need for multiple components and interconnections, which can enhance reliability and reduce assembly costs. A study published by IPC (Institute of Printed Circuits) notes that the use of rigid flex designs can lead to a reduction in overall product weight by up to 50%, while improving the durability of the electronic device. Furthermore, the integration of these circuits allows for greater design flexibility, enabling engineers to develop innovative products that meet the needs of industries such as telecommunications, automotive, and medical devices. As technology continues to advance, the role of rigid flex rigid PCBs in shaping the future of electronics will undoubtedly become even more significant.
What is Rigid Flex Rigid PCB?
Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs combine the best features of rigid and flexible printed circuit boards, offering a versatile solution for modern electronic applications. These PCBs are designed to withstand the rigors of various environments while maintaining reliable performance. By integrating rigid sections for component placement and flexible areas for complex shapes, they provide both durability and flexibility. This unique combination allows for efficient space utilization in compact devices such as smartphones and automotive electronics.
The benefits of Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs extend beyond just physical flexibility; they can significantly improve the overall reliability of electronic systems. With fewer interconnections and reduced potential failure points, these PCBs contribute to enhanced durability and performance. As the automotive PCB market is projected to grow from $9.15 billion in 2023 to $15.1 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 5.9%, incorporating Rigid Flex technology will be crucial for meeting the increasing demand for advanced electronic features in vehicles. This growth highlights the importance of innovative PCB designs in the evolving landscape of modern electronics.
History and Evolution of Rigid Flex Rigid PCB Technology
Rigid flex PCBs have undergone significant evolution since their inception in the late 20th century. Initially developed to support the burgeoning demand for compact and lightweight electronic devices, rigid flex technology has become a crucial component in diverse applications, ranging from aerospace to medical devices. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global rigid flex PCB market is projected to reach $27.92 billion by 2026, indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.7% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by the increasing miniaturization of electronic components and the demand for higher reliability in advanced technology applications.
The historical evolution of rigid flex PCBs can be traced back to the integration of flexible substrates in traditional PCB designs. In the 1980s, companies began exploring the synergistic benefits of combining rigid and flexible materials, which led to the development of the first rigid flex boards. Over the years, advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques have significantly enhanced their performance, enabling manufacturers to create boards that can withstand rigorous environments while maintaining functionality. By the 2010s, rigid flex PCBs had become dominant in sectors such as consumer electronics and telecommunications, providing manufacturers with the ability to innovate new products that require complex geometries and reduced weight without compromising on electrical performance.
Benefits of Rigid Flex PCBs Over Time
Key Components and Structure of Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs
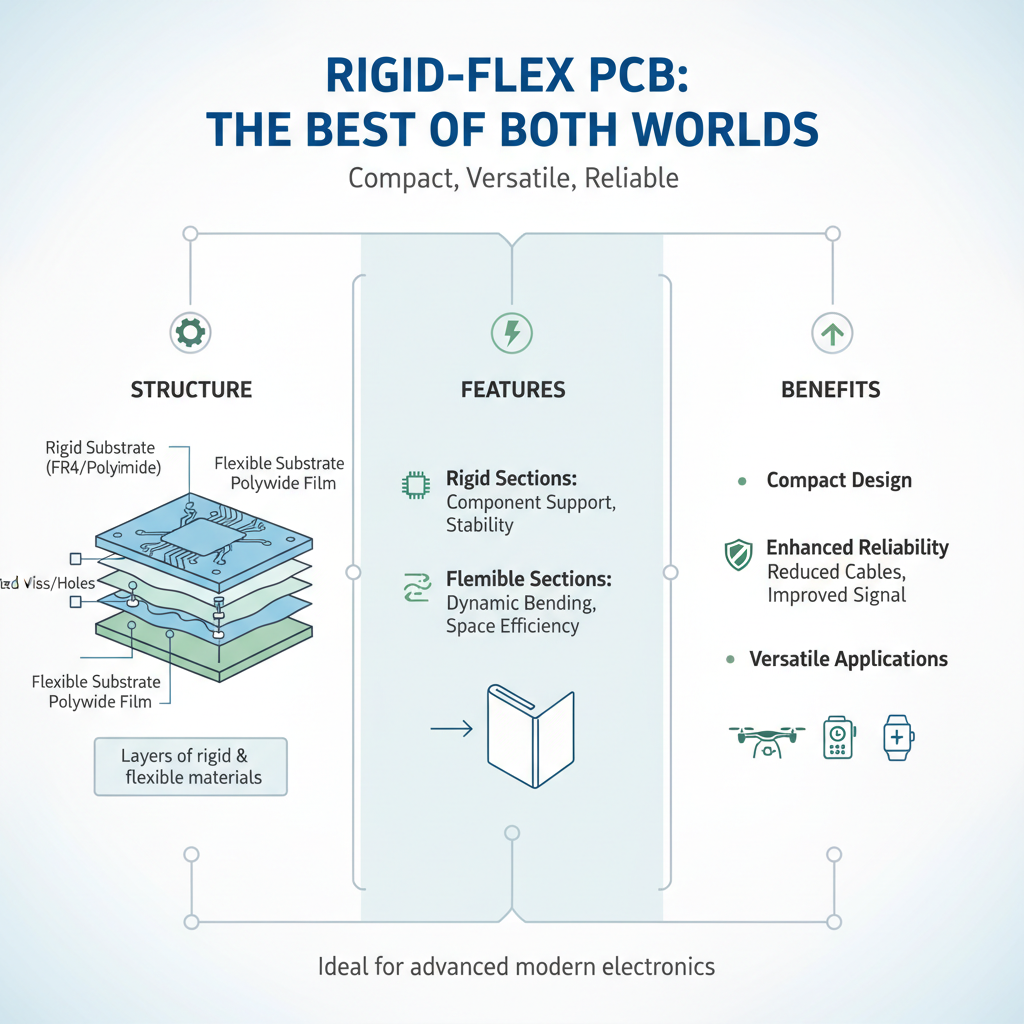
Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs combine the advantageous features of both rigid and flexible circuits, allowing for a compact and versatile design in modern electronics. The structure fundamentally consists of multiple layers: rigid and flexible substrates are layered together, interconnecting through plated holes or vias. The rigid sections provide sturdiness and support for critical components, while the flexible parts enable dynamic movement and bending, making these PCBs ideal for devices requiring mobility and space efficiency.
Key components of Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs include the dielectric layers, copper traces, and protective coatings. The dielectric layers, often made from materials like polyimide, contribute to the flexibility and insulation, while copper traces facilitate electrical connections across both the rigid and flexible regions. Additionally, the protective coatings shield the circuitry from environmental factors, enhancing durability. This combination of materials and structure allows for innovative applications, such as in smartphones, wearable devices, and medical equipment, where space-saving and reliability are paramount.
Advantages of Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs in Modern Electronics
Rigid flex PCBs are increasingly gaining traction in modern electronics due to their unique advantages, particularly in the context of miniaturization. The industry is undergoing a significant transformation, emphasizing more compact designs that enhance efficiency and reliability across various applications. According to the multilayer printed circuit board market analysis for 2032, the demand for rigid flex designs is anticipated to rise, driven by their inherent ability to save space while offering robust performance. These boards enable seamless integration into tight spaces, making them ideal for consumer electronics, medical devices, and aerospace applications.
One compelling benefit of rigid flex PCBs is their ability to facilitate flexible micromachined ultrasound transducers in biomedical applications. This technology exemplifies how miniaturization and flexibility converge to improve imaging quality in medical diagnostics. Additionally, research on biodegradable substrates for electronic components indicates a growing trend towards sustainable solutions, aligning with the need for greener electronics.
Tips: When designing with rigid flex PCBs, consider the potential for reduced assembly complexity and improved mechanical reliability. Furthermore, always evaluate the long-term environmental impact of materials used, aiming for greener alternatives where possible. Embracing the advancements in PCB technology will help drive innovation in your projects while ensuring efficiency and sustainability.
What is Rigid Flex Rigid PCB and How it Benefits Modern Electronics
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Space Efficiency | Combines rigid and flexible PCB areas. | Reduces the overall size of electronic devices. |
| Design Flexibility | Flexible portions can bend and move. | Allows for innovative designs and unique applications. |
| Weight Reduction | Lightweight materials used in flexible sections. | Decreases device weight, enhancing portable applications. |
| Durability | Resistant to shocks and vibrations. | Increases longevity of electronic products. |
| Thermal Management | Improves heat dissipation through PCB design. | Keeps components cooler, enhancing performance and reliability. |
Applications of Rigid Flex Rigid PCBs Across Various Industries
Rigid flex rigid PCBs have become increasingly important across various industries due to their unique ability to combine the flexibility of flexible circuits with the robustness of rigid boards. This hybrid technology allows for compact designs and improved performance in space-constrained applications, making them ideal for modern electronic devices in sectors such as automotive and consumer electronics. According to industry reports, the global automotive PCB market is projected to grow from $9.15 billion in 2023 to $15.1 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9%. This growth reflects the rising demand for advanced electronics in vehicles, where rigid-flex PCBs play a critical role.
The adoption of rigid flex PCBs extends beyond the automotive industry; they are also utilized in aerospace, medical devices, and telecommunications. The need for reliable and lightweight components in these fields drives innovation and application of rigid flex technology. For instance, as manufacturers optimize electronic designs to ensure durability and efficiency, rigid flex PCBs offer a solution that facilitates miniaturization while enhancing signal integrity. As regions like India impose anti-dumping duties on printed circuit boards from China, local manufacturers may face challenges, but the overall growth trend in PCB technology signifies a robust future across various applications.
Related Posts
-
Top 5 Benefits of Using Flex Circuit Boards in Modern Electronics
-
2025 Guide: How to Choose the Best Flexible PCB Manufacturing Services
-
Understanding the Importance of Flexible Printed Circuits in Modern Electronics
-
Unlocking the Future of Circuit Board Production with Sustainable Practices and Advanced Technologies
-
The Future of PCB Manufacturing Innovations Transforming Electronics Industries
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Flexible PCBs for Your Project
