Why Rigid PCB Is Essential for Modern Electronics Development?
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, rigid PCBs play a crucial role in development. Their reliability and performance make them ideal for various applications. Rigid PCBs provide the stability needed for complex circuits. They support multiple layers and intricate designs. As devices become smaller and smarter, these boards ensure durability.
However, the demand for innovation also poses challenges. Manufacturers must adapt to new technologies continuously. Rigid PCBs must be balanced with advancements in materials and design practices. This can be tricky. Not every new development works seamlessly with existing PCB technologies. Design flaws may arise, amplifying risk.
Flexibility in design is essential yet difficult to achieve without compromising quality. Engineers must reflect on their processes. They have to consider alternative materials and configurations. Past mistakes guide the way forward. Recognizing the limitations of rigid PCBs is vital for future advancements. The journey of improvement never truly ends.
Importance of Rigid PCBs in the Electronics Industry
Rigid PCBs play a crucial role in the electronics industry. They provide structural integrity and reliability, essential for modern devices. According to a report by Research and Markets, the rigid PCB market is projected to grow significantly, with a CAGR of over 5% through 2025. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for consumer electronics and automotive applications.
Rigid PCBs are essential for various applications, including smartphones, computers, and industrial machinery. Their ability to support dense component placement is vital. This means they can accommodate advanced features in smaller sizes. Yet, not all rigid PCBs are created equal. There are differences in materials, thickness, and manufacturing processes that can affect performance.
**Tips:** Ensure to assess your specific design needs. Consider factors like thermal management and electrical performance. Also, test prototypes thoroughly before mass production. This will help identify potential issues early on. Remember, even minor flaws can lead to significant failures in sensitive electronics. Be mindful of this during the design phase.
Why Rigid PCB Is Essential for Modern Electronics Development
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Stability | Rigid PCBs provide a stable platform for electronic components, ensuring reliability and durability. |
| Heat Resistance | They can withstand higher temperatures, making them suitable for demanding environments. |
| Manufacturing Precision | Rigid PCBs allow for precise manufacturing, reducing the risk of defects in high-density applications. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | These boards are generally less costly to produce compared to flexible alternatives, making them a common choice. |
| Versatility | Used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. |
| Integration | Rigid PCBs accommodate numerous components and can integrate complex circuits effectively. |
Key Advantages of Rigid PCBs Over Other Board Types
Rigid PCBs are crucial in modern electronics. They offer unique advantages that support various applications. One key benefit is their structural integrity. Rigid boards remain stable and reliable even under mechanical stress. This property is vital in industries like aerospace and automotive, where safety is paramount. Research indicates that rigid PCBs account for over 60% of the global PCB market. This figure highlights their importance in device performance.
Another advantage of rigid PCBs is their heat dissipation capabilities. Unlike flexible boards, rigid designs can effectively manage heat, extending the lifespan of electronic components. Data from industry reports show that devices with rigid PCBs have a 20% longer operational life compared to those with flexible alternatives. However, using rigid boards can lead to challenges, like limited flexibility in design. As technology advances, this limitation demands attention.
Lastly, rigid PCBs provide better signal integrity. They minimize interference through improved electromagnetic performance. Many high-frequency applications prefer rigid configurations for this reason. Yet, achieving optimal performance requires careful design. Balancing rigidity and functionality can be a complex task. Ensuring high quality while adapting to ever-changing technology needs continuous evaluation.
Advantages of Rigid PCBs in Modern Electronics
Applications of Rigid PCBs in Modern Electronic Devices
Rigid Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in modern electronic devices. From smartphones to medical equipment, these boards provide the necessary stability and durability. According to industry reports, the global PCB market is expected to reach $93 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by increasing demand for electronics across various sectors.
In smartphones, rigid PCBs support multi-layer designs. This allows for compact components, giving more space for advanced features. Medical devices also heavily rely on rigid PCBs. The precise alignment and robustness ensure reliability in critical applications. Expect to see sensors and circuits integrated more tightly, enhancing functionality.
Tip: Consider the thermal management of your rigid PCB. Some designs overlook heat distribution, leading to performance issues.
In the automotive sector, rigid PCBs are vital. They ensure safe operations of systems like navigation and safety controls. However, the complexity sometimes leads to challenges in manufacturing and repair. Often, the focus on compact designs can compromise easy access for maintenance. A balance is essential to ensure both performance and serviceability.
Tip: Don’t neglect redundancy features. They can be lifesavers in high-stakes environments.
Materials and Manufacturing Processes for Rigid PCBs

Rigid PCBs are crucial for modern electronics. They offer durability and stability, which is vital for various applications. The typical materials used in rigid PCB manufacturing include FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. According to a recent industry report, FR-4 accounts for about 80% of the PCB market share. This demonstrates its significant role in ensuring performance standards.
The manufacturing process of rigid PCBs involves several steps. It begins with patterning the copper layer and then etching away the unwanted copper. Recent advancements, like robotic arms, enhance efficiency but sometimes sacrifice precision. In 2022, a survey indicated that nearly 25% of PCB manufacturers reported issues during the etching process. This raises questions about how to minimize errors in manufacturing.
Thermal management is another challenge. Rigid PCBs generate heat during operation, and improper management can lead to failures. A study revealed that 15% of electronic device failures are linked to thermal issues. Engineers must carefully consider material choices to mitigate these risks. Balancing performance and production costs is complex. This coexistence of innovation and potential pitfalls continues to shape the rigid PCB landscape.
Future Trends in Rigid PCB Technology and Innovation
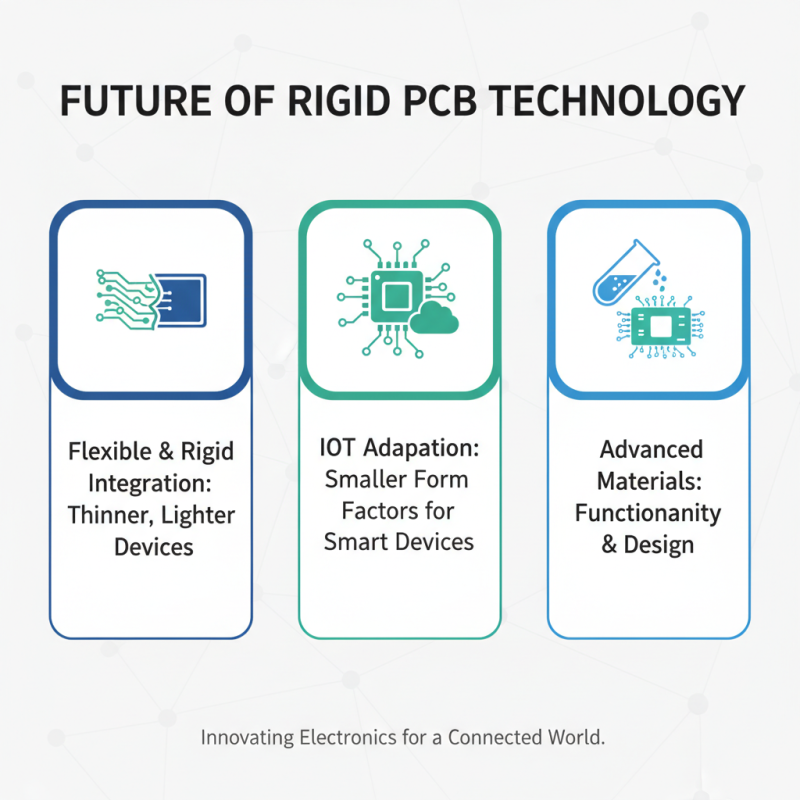
The future of rigid PCB technology is exciting and full of potential. Innovations in materials are transforming the way we design electronics. For instance, flexible materials are being integrated into rigid PCB structures. This blending enhances functionality, allowing for thinner and lighter devices. With the rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, rigid PCBs are adapting to new requirements. Smaller form factors are now a priority for engineers.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming essential in the PCB industry. Manufacturers are exploring eco-friendly materials that reduce environmental impact. The challenge lies in balancing performance and sustainability. Some rigid PCBs may still rely on traditional processes that are not environmentally sound. There’s a need for the industry to push boundaries and develop cleaner methods.
The integration of artificial intelligence is another trend. Smart adhesives and soldering techniques are emerging. They promise better connectivity and reliability. However, this technology is not without its flaws. Some solutions may cause more issues than they solve. Engineers must carefully consider the longevity and maintenance of such innovations. The path forward requires reflection on both the opportunities and the hurdles that rigid PCB technology presents.
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Benefits of Using PCB Boards in Electronics Manufacturing
-
Top Reasons to Choose PCB Rigid Flex for Your Next Electronics Project
-
Unlocking Innovation: The Future of Circuit Board Design in 2024 and Beyond
-
The Future of PCB Manufacturing Innovations Transforming Electronics Industries
-
Understanding PCB Production: Essential Insights for Future Electronics Innovators
-
Top 7 Most Innovative Techniques in Circuit Board Production You Need to Know
